|
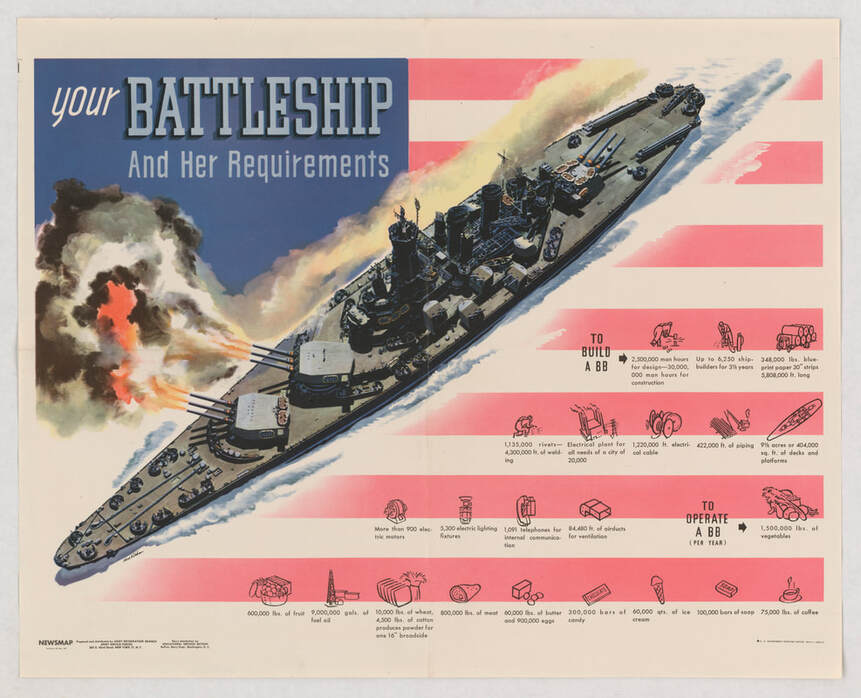
Last World War Wednesday, we looked at the use of ice cream in the U.S. Navy during the First World War, especially aboard hospital ships. Now it's time for a reprise! By the Second World War, ice cream was firmly entrenched aboard Naval vessels. So much so, that battleships and aircraft carriers were actually outfitted with ice cream machinery, and by the end of the war the Navy was training sailors in their uses through special classes. The above propaganda poster, courtesy the National Archives, outlines all of the requirements to build a battleship. "Your Battleship and Her Requirements" may have been targeted toward factory workers, but I think it is more likely this poster was designed to impress upon ordinary Americans the extraordinary amount of materials and supplies needed to keep a battleship in fighting trim. What I found particularly interesting, was that among the supplies listed, alongside fruits and vegetables and meat and even candy, was 60,000 quarts of ice cream! Smaller vessels, such as destroyer escorts and submarines, did not have the space for their own ice cream making machinery, although they did have freezers. In fact, it became common for destroyer escorts and PT boats to rescue downed pilots (the aircraft carries were too big for the job) and "ransom" them for ice cream. Last week a brand new food podcast debuted for American Public Television called "If This Food Could Talk," and I'm so pleased to say I was featured in the first episode, "Frozen in Time: Ice Cream and America's Past." I had a blast doing the research for that episode's interview, which has inspired these two recent World War Wednesday posts. Have a listen if you want to learn more about ice cream in American history, and especially the story of ice cream in the Navy. But while I was doing the research, I kept running across references to ice cream as a health food! The National Dairy Council really leaned into the notion of ice cream and the armed forces. This advertisement reads, "There's a reason why the U.S. Navy serves Ice Cream. America's favorite dairy food - Ice Cream - is an important source of vitamins, proteins and minerals." The ad goes on: "Navy menus don't just happen! Every food included in the diet of Navy personnel, ashore or afloat, is there for a purpose. It is there because it has been okayed by the staff of experts at the Subsistence Research Laboratory of the U.S. Navy in Chicago for making an important contribution to the health, strength, and morale fighters must have to win! "These highly skilled and trained technicians at the laboratory know every condition under which the men live - know their requirements - and make sure exactly what each food will do for those men before it is approved. "That is why it is significant that ice cream ranks so high on Navy menus. It is not only a favorite food, but it also supplies valuable vitamins, proteins, and minerals. For that reason, wherever practical, the Navy gets ice cream! "Throughout the world - over the seven seas - the talents of the Subsistence Research Laboratory of the U.S. Navy are directed to keeping our Navy a strong, healthy, hard-hitting force; making sure it gets the foods the men like - the foods they need for victory! "Ice Cream Is a Fighting Food "Ice cream is a favorite with all branches of our armed forces - and it is important that they get this valuable food. So fi you aren't always able to get all the ice cream you want - remember, you're 'sharing' this nutritious food with our fighters." The National Dairy Council might be just a SMIDGE biased in this regard, but certainly the federal government ranked milk, and by extension milk products, very highly in terms of nutrition during the Second World War, notably as part of the Basic 7 nutrition recommendations. This was almost certainly a holdover from the Progressive Era's take on milk as the "perfect food" - combining proteins, carbohydrates, and fats all in one. We see this in another advertisement, this time by the National Dairy Products Corporation. The National Dairy Council is an industry-funded research and marketing organization. But the National Dairy Products Corporation would later become Kraft Foods. "Here's what one leatherneck dreams about! "One Marine's dream of the post-war world is a mountain of strawberry ice cream. He wrote his girl from Guadalcanal that he wants it three times a day, every day for five years. In standard servings, that's over 900 quarts! "Strawberry ice cream was a symbol, of course, to a hot, tired fighting man in a fox-hole - a symbol of his home town and the corner drug store - a symbol of America. It must have appealed to lots of folks, for many newspapers carried the story. "There are good reasons why ice cream is on Army menus regularly - good reason why busy war workers eat so much of it. It is more than a delicious dessert - it's a valuable food - rich in vitamins and calcium. "Right now, of course, ice cream must come from the same milk supply that furnishes milk, cream, butter and cheese to soldiers, civilians and allies alike. That means less ice cream for your family's use. If you'll be content with your fair share - if you'll accept part of your order in fruit ices - you can continue to enjoy ice cream. "And we'll continue to improve ice cream processing and packaging - controlling its quality - keeping it pure and good. "We'll continue our intensive laboratory research... developing important new products from milk... bringing to America's fighters, workers and friendly allies the full benefits of nature's most nearly perfect food." Here you can see the "perfect food" rhetoric in action! And interestingly, this one touts the role of ice cream in the Army as well. In my opinion ice cream, for all the rhetoric about nutrition, had far more to do with morale than anything else. But there is some truth to the idea that as a dessert it was superior to cake or pie. For one thing, ice cream does have some protein, in addition to a decent amount of fat. Full fat dairy is generally proven to be more filling and satisfying and protein and fat slow down the absorption of sugar directly into the bloodstream, making the "energy-giving" properties of carbohydrates longer-lasting and less likely to make you crash (unlike cake and cookies). That being said, viewing ice cream as a health food is questionable today. But in the period, the discoveries of vitamins and minerals like calcium were cutting-edge, and any food containing those essential nutrients was considered good for you. Ice cream also fit neatly into ideas (unconscious or otherwise) of White supremacy and American (i.e. Anglo-Saxon) culture. As the National Dairy Products Corporation marketing team wrote, ice cream was "a symbol of America." When combined with soda fountains (the wholesome, if sugary, alternative to saloons and beer halls), ice cream seemed to represent the best of America - slim, good-looking, young, White America, that is. Today, ice cream's modern accessibility has given us ice cream alternatives aplenty, especially for folks who can't consume dairy. Ice cream's ubiquity has also meant some of its luster has faded. But at a time of extreme stress - the violence of the theater of war, the privations of home front rationing, the push to mobilize for total war, the fear of invasion - ice cream provided a moment of bliss in the midst of uncertainty. Ice cream is still an essential tradition aboard Naval vessels today. When you're miles from home for months at a time, anything that seems like a treat gives morale a boost. It's still a treasured treat in our household, whether homemade or store bought (if you find yourself in upstate New York - do yourself a favor and seek out Stewart's Shops. They have the best commercial ice cream around). What does ice cream mean to you? The Food Historian blog is supported by patrons on Patreon! Patrons help keep blog posts like this one free and available to the public. Join us for awesome members-only content like free digitized cookbooks from my personal collection, e-newsletter, and even snail mail from time to time! A special patrons-only post is coming tomorrow with more on ice cream in World War II - this time featuring Elsie the Cow! Join now for as little as $1/month.
Don't like Patreon? Leave a tip!
1 Comment
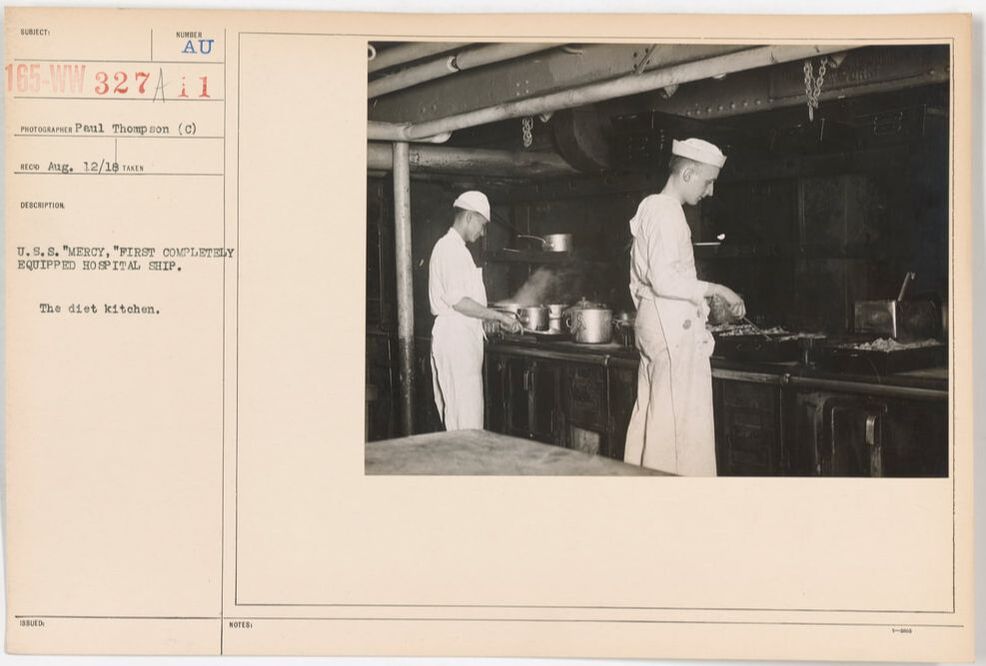
I've been getting a lot of calls for information about ice cream lately, and that has sent me down a rabbit hole. I did a whole talk on the history of ice cream last year (you can watch the filmed version here), but while I knew ice cream was a big tradition in naval history, I didn't know the connection to the First World War. I don't usually cover the history of military consumption of food during the World Wars, but this topic was just too much fun to resist. Ice cream wasn't always the Navy's treat of choice. For over a hundred years rum was the preferred ration by many sailors. But in the late 19th century the Temperance movement began to have increasing power over society. By 1919 we had a Constitutional Amendment (the 19th - often known just as "Prohibition"). But the armed forces went dry much earlier. In particular, on July 1, 1914, the U.S. Navy went alcohol-free. At the same time, naval vessels were being stocked with ice cream. In the May, 1913 issue of The Ice Cream Trade Journal, an article entitled "Sailors Like Ice Cream" explained that the Navy had recently ordered 350,000 pounds of evaporated milk - ostensibly for all sorts of cooking and baking, but ice cream was high on the list. You may wonder why hospital ships in the First World War were manufacturing ice cream on board? Well, it involves multiple factors. First is that ice cream was a product of milk; during the Progressive Era, milk was considered the "perfect food" as it contained fats, proteins, and carbohydrates all in one (supposedly) easily digestible package. Although many people are lactose intolerant, the White Anglo-Saxon dominance of American culture at the time prized milk. Ice cream rode into nutritional value on the coattails of milk. During this time period, dairy-based products like puddings, custards, milk and cream on cooked cereals or with toast, and ice cream were all considered nutritious foods for people who had been injured or ill. Along with foods like beef tea, eggs, and stewed fruits, these made up the bulk of recommended hospital foods from the late 19th century to World War I. Ice cream shows up quite frequently in early reports of the Surgeon General to the U.S. Navy. In his 1918 report to the Secretary of the Navy, ice cream appears to cause more problems than it solves. Notably, the use of ice cream produced commercially results in several instances of crew sickness, including simple illnesses like strep throat, alongside more serious ones like a diphtheria outbreak in Newport in 1917, which was traced to ice cream produced off-station. Fears of the spread of typhoid from places like restaurants, soda fountains, and ice cream shops led to "antityphoid inoculations" at naval shipyards. In Chicago, "All soft-drink and ice-cream stands have promised to give sailors individual service in the form of paper cups and dishes. To make this more effective, it is believed that an order should be issued prohibiting men from accepting any other kind of service." The Surgeon General also recommended inspection of offsite dairies and bottling works for milk, ice cream, and soft drinks to ensure proper sterilization of equipment and pasteurization of dairy products, as well as inoculation of employees against typhoid and smallpox. But ice cream was also noted as essential not only on the existing hospital ship USS Solace, but also on two new hospital ships fitted out since the declaration of war in 1917 - the USS Mercy and the USS Comfort. These ships included a cold storage plant and a refrigerating machine that could "produce, under favorable circumstances, a ton of ice or more a day." The ships also had distilling plants, able to convert seawater to fresh water, up to 20,000 gallons per day. In addition to describing the medical wards, crew facilities, laundry, and kitchen, the report noted: The most valuable adjunct in the treatment and feeding of the sick is the milk emulsifier, popularly known as the "mechanical cow." The milk produced from this machine is made from a combination of unsalted butter and skimmed milk powder and can be made with any proportion of butter fat and proteins desired. This machine will produce 15 gallons of cold, pasteurized milk in 45 minutes. The electric ice cream machine, controlled by one man, makes 10 gallons at a time and is supplemented by small freezers for preparing individual diets for the sick. According to the October, 1918 issue of The Milk Dealer, the "mechanical cow" had been displayed as part of the exhibits at the National Dairy Show in Columbus, Ohio in the fall of 1917. They noted: The "Mechanical Cow" Becoming Famous. Few people who saw the combination exhibit of Merrell-Soule Co. and the DeLaval Separator Co., last October, in Columbus, would have believed that within a year from that beginning the use of the Emulsor in combining Skimmed Milk Powder, unsalted butter and water would be taken up by Army, Navy, City Administrations, etc. throughout the United States. Such is the fact, however. The Mechanical Cow is now producing milk and cream on the U.S.S. Comfort and U.S.S. Mercy, the two splendid hospital ships of the Navy. An installation on board the U.S.S. South Carolina is kept working continuously to supply the demands of her crew. Mechanical Cows are filling the needs of milk at the base hospitals and several camps and one large machine is being operated by one of the city departments of New York. Health officers, physicians, milk experts and authorities on infant feeding all unanimously agree that milk and cream made by means of the "Mechanical Cow" is superior in every way to the average milk supply. This advertisement for "The Chilly King," a cooling machine that was part of the "Mechanical Cow" system on ships like the U.S.S. Mercy (a photograph of the machinery on board featured in the ad) also names a number of naval ships and military camps which use it, including:
By enabling ships and camps to use shelf-stable skimmed milk powder and unsalted butter, which keeps a very long time in cold storage, "mechanical cows" allowed for an ample supply of milk made in sanitary conditions. For naval ships, this was especially important when crews were away from shore for long periods of time. Ice cream also helped patients recover from illness (or so medical professionals at the time believed) but it also helped a great deal with morale. The professionalization of ship operations via the installation of state-of-the-art equipment was a hallmark of the First World War, but the U.S.'s late involvement in the war hamstrung most shipbuilding operations. Indeed, the construction of a new hospital ship in 1916 was actually shelved in favor of retrofitting existing ships like those that were transformed into the U.S.S. Comfort and U.S.S. Mercy, which had initially served as the sister passenger steamboats S.S. Havana and S.S. Saratoga, respectively. Part of the Ward Line, these very fast steamships ran the New York City to Havana, Cuba route but were requisitioned in 1917 first as troop transports, and later as hospital ships. The U.S.S. Mercy spent time as a home for the homeless during the Great Depression before she was scrapped in the 1930s, and the U.S.S. Comfort went back to civilian passenger transport for the Ward line under her old name, the S.S. Havana, before being pressed into service again in World War II, this time as a troop transport once again. The names USS Comfort and USS Mercy would be revived in World War II and a third pair of hospital ships bearing those names are still in operation today. Although ice cream is no longer considered central to the recuperation of the sick and wounded, it is still served on American naval vessels around the world. Ice cream would play an even more important role in the Navy during the Second World War. But that's a tale for another World War Wednesday! The Food Historian blog is supported by patrons on Patreon! Patrons help keep blog posts like this one free and available to the public. Join us for awesome members-only content like free digitized cookbooks from my personal collection, e-newsletter, and even snail mail from time to time! Don't like Patreon? Leave a tip!
I can take zero credit for coming up with this genius recipe. That 100% goes to Nevada and her North Wild Kitchen, which is where I first found her recipe for rømmegrøt ice cream. You may be asking yourself, what on earth is rømmegrøt? Rømmegrøt is a traditional Norwegian porridge made from flour and heavy cream, usually served with cinnamon and sugar at Christmastime. The term rømmegrøt means "sour cream porridge," and in Norway the traditional recipe often calls for a mixture of sour cream and milk. But for whatever reason, here in the States, it is almost exclusively made with plain heavy cream. Interestingly, as far as I can tell, the taste is not particularly different, because this ice cream is made with sour cream and it tastes exactly like the rømmegrøt I grew up eating. (If you're interested in the original rømmegrøt, check out my patrons-only post on Patreon, complete with a recipe!) The "real" rømmegrøt is incredibly rich. The flour makes for a smooth, creamy pudding-like texture and as it cooks with the heavy cream it "splits" and "makes" its own melted butter sauce as the flour binds to the dairy proteins in the heavy cream. Historically its richness made it the perfect food for winter holidays, which is why it is so often associated with Christmas. This is also perhaps why soured cream was used, instead of fresh. Cows generally stop producing milk once their offspring are weaned, so winter is the time a lot of cows would "dry up" until they got pregnant again. If a family only had one cow, it would be impossible to get fresh dairy year-round. Rømmegrøt is also a traditional dish for new mothers - the rich but easily digested food helped them recover from the trauma of childbirth, and ensured they got enough calories to keep their babies well-fed. But while this food is, indeed, delicious, eating a rich, stick-to-your-ribs dish in the summer heat is not exactly appealing. Enter the genius rømmegrøt ice cream. Any purchases from links below will result in a small commission for The Food Historian. Rømmegrøt Ice CreamI'm giving you this recipe because although Nevada's North Wild Kitchen recipe is marvelous, I tweaked hers just a little. Fair warning that you will need an ice cream maker for this one. (We got this one as a wedding present and love it.) 12 ounces full fat dairy sour cream (1/2 of a 24 ounce carton) 1 1/2 cups heavy cream 3/4 cup granulated sugar 1/2 teaspoon ground cinnamon In a pourable container, mix all ingredients and whisk well to combine (you could stop at this point and just eat the pourable mix with a spoon, and I always lick the bowl). Pour into the ice cream maker and start. When the ice cream is no longer turning over in the maker, it's pretty much done. You can pack it into a freezer container (these are nice) or serve immediately. Rømmegrøt ice cream has a tangy sweet flavor and including the cinnamon in the ice cream makes all the difference, for me. You can eat it on its own, but it also pairs well with apple pie or crisp, blueberry, blackberry, rhubarb, or strawberry desserts, and gingerbread. I had originally intended to make a big strawberry rhubarb crisp for the party to go with this ice cream, but ran out of time. And since I made two batches of rømmegrøt ice cream in advance, it almost got forgotten altogether! I pulled it out last minute for anyone who had room for a little more dessert. While everyone enjoyed it, I think I was the only one who had ever tasted rømmegrøt before, so perhaps it's slightly less of a delight without the taste memories to work with. I guess this just means I'll have to throw a Scandinavian Christmas party to introduce everyone to the joys of original rømmegrøt! The Food Historian blog is supported by patrons on Patreon! Patrons help keep blog posts like this one free and available to the public. Join us for awesome members-only content like free digitized cookbooks from my personal collection, e-newsletter, and even snail mail from time to time! Don't like Patreon? Leave a tip! |
AuthorSarah Wassberg Johnson has an MA in Public History from the University at Albany and studies early 20th century food history. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed