|
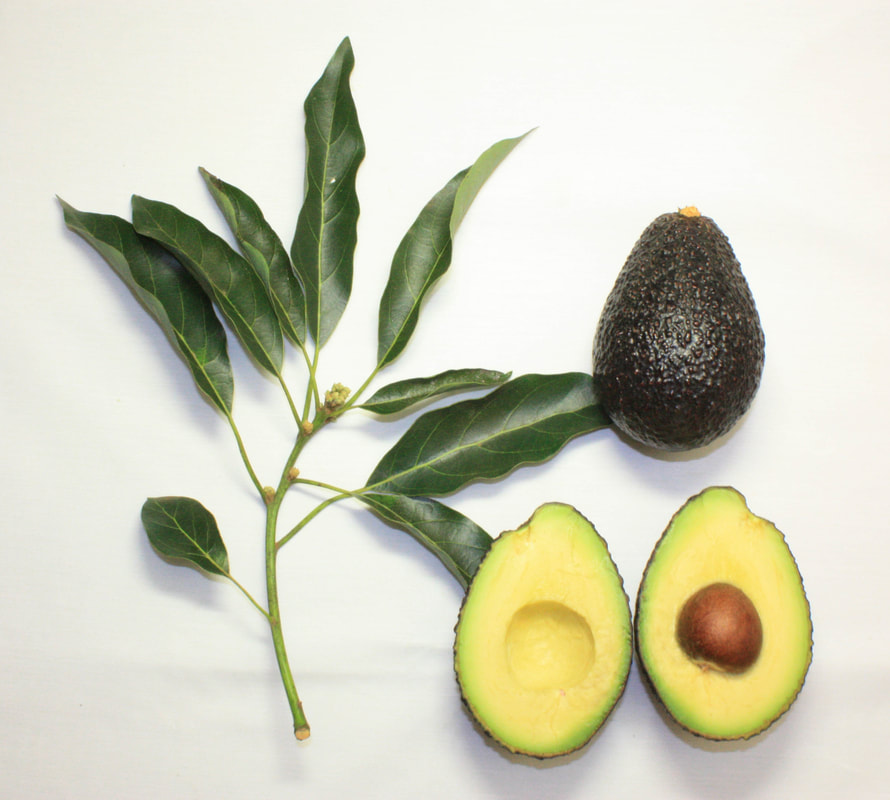
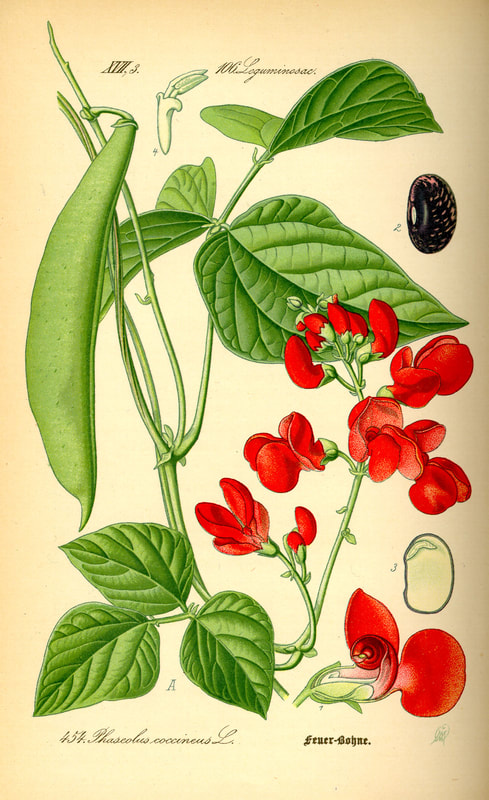
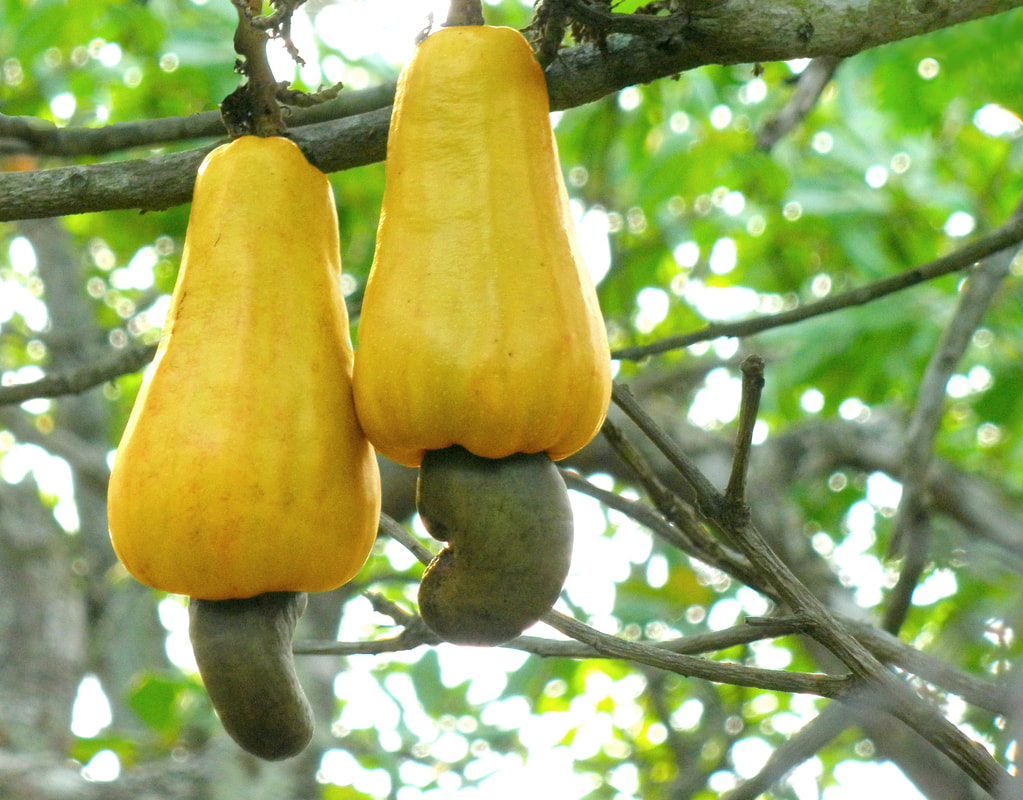
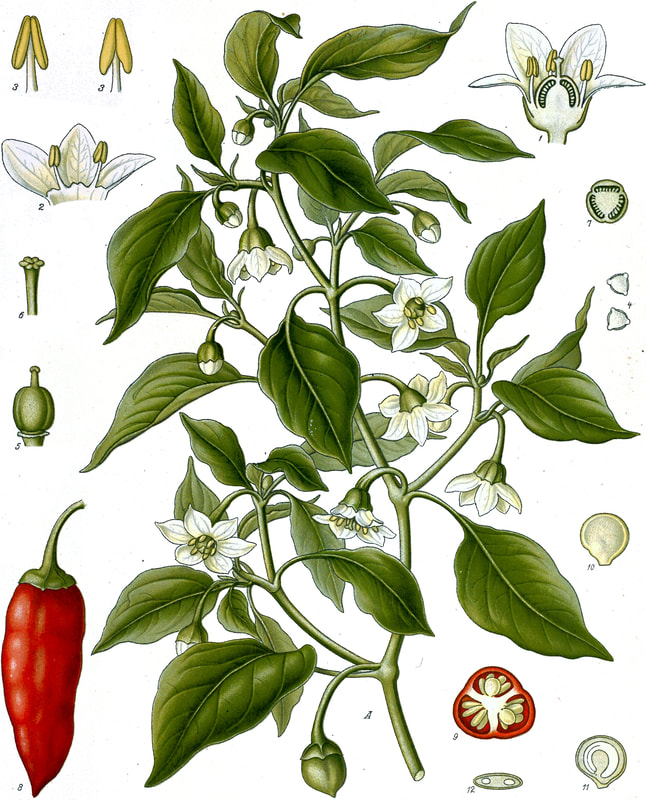
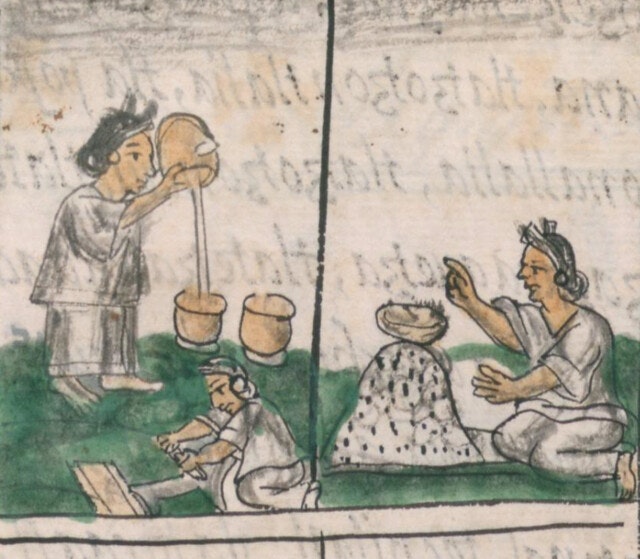
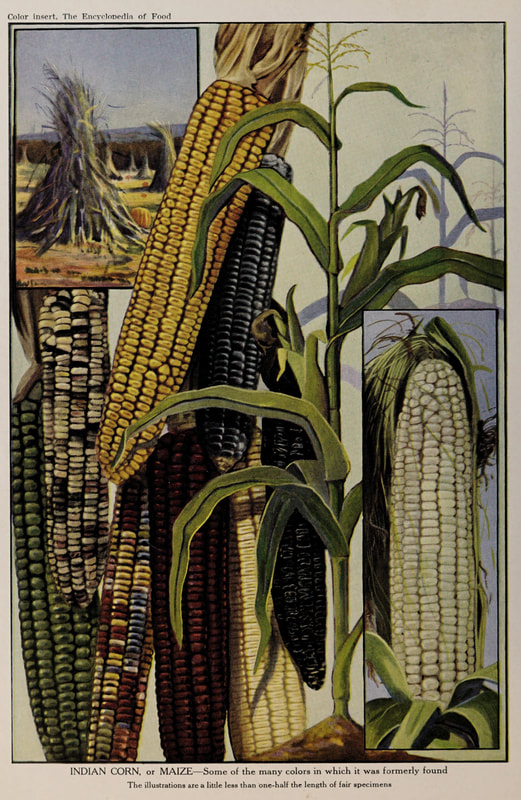
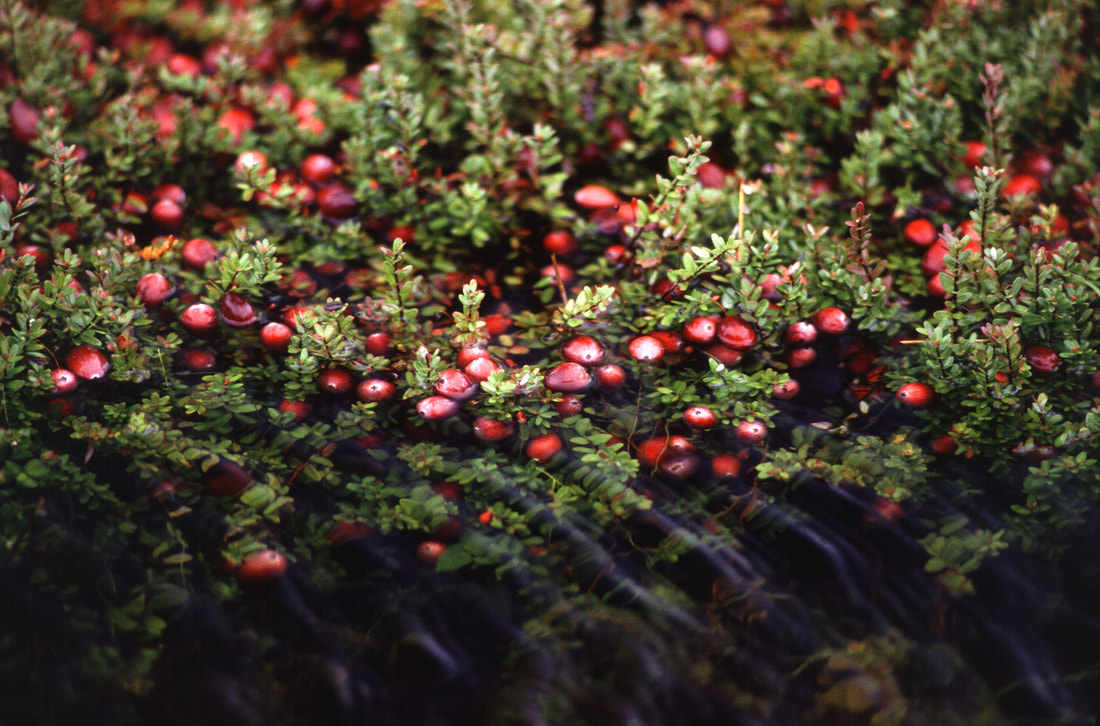
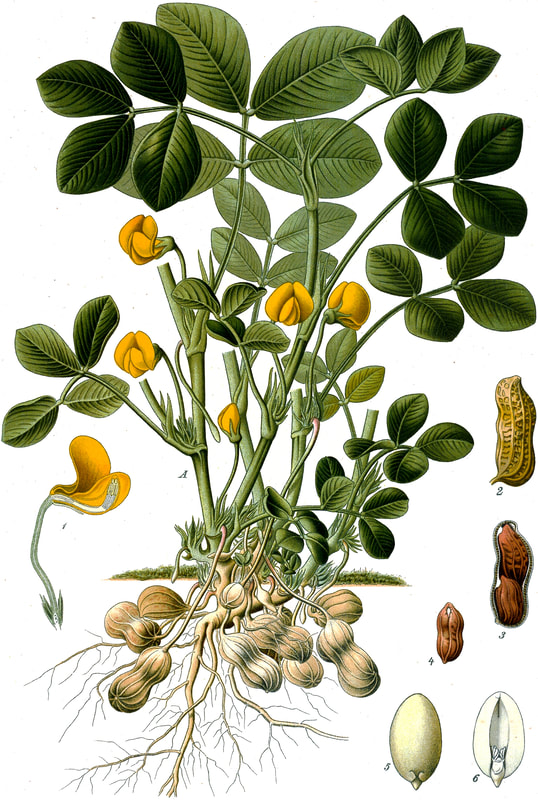
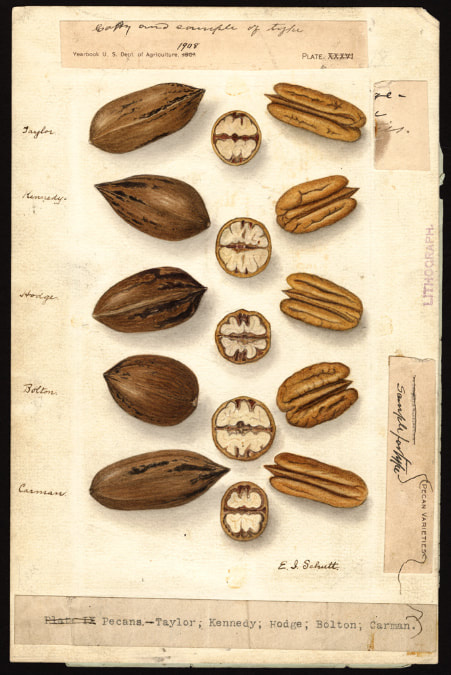
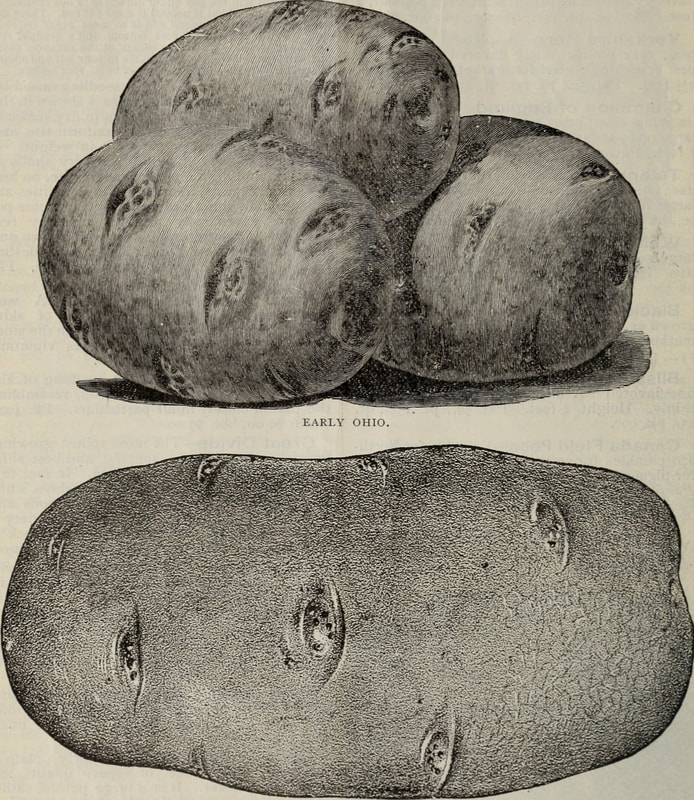
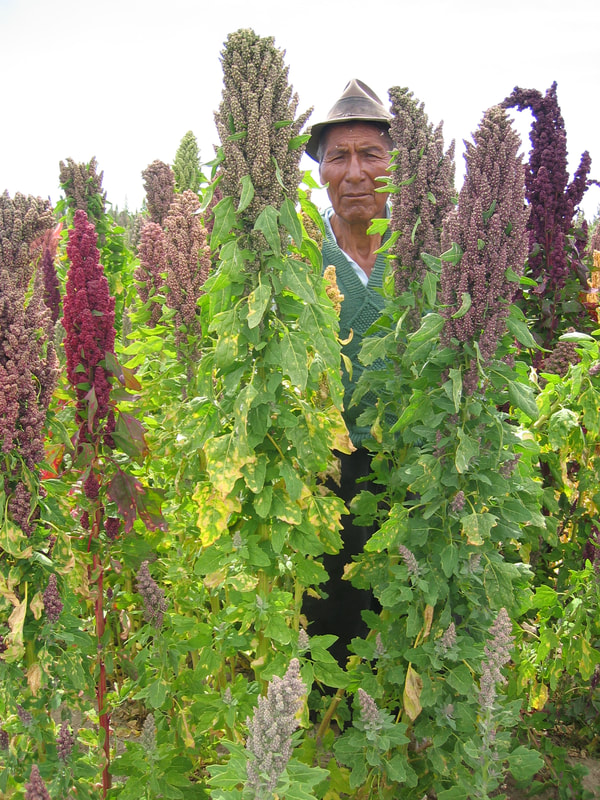
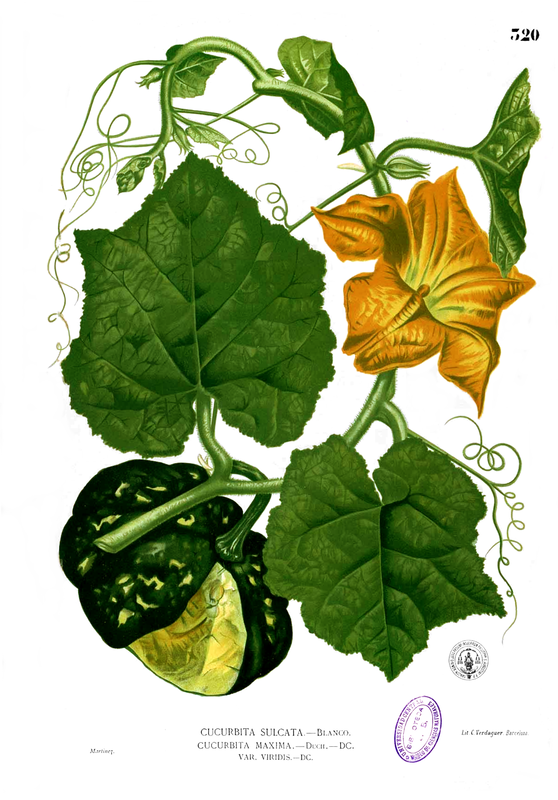
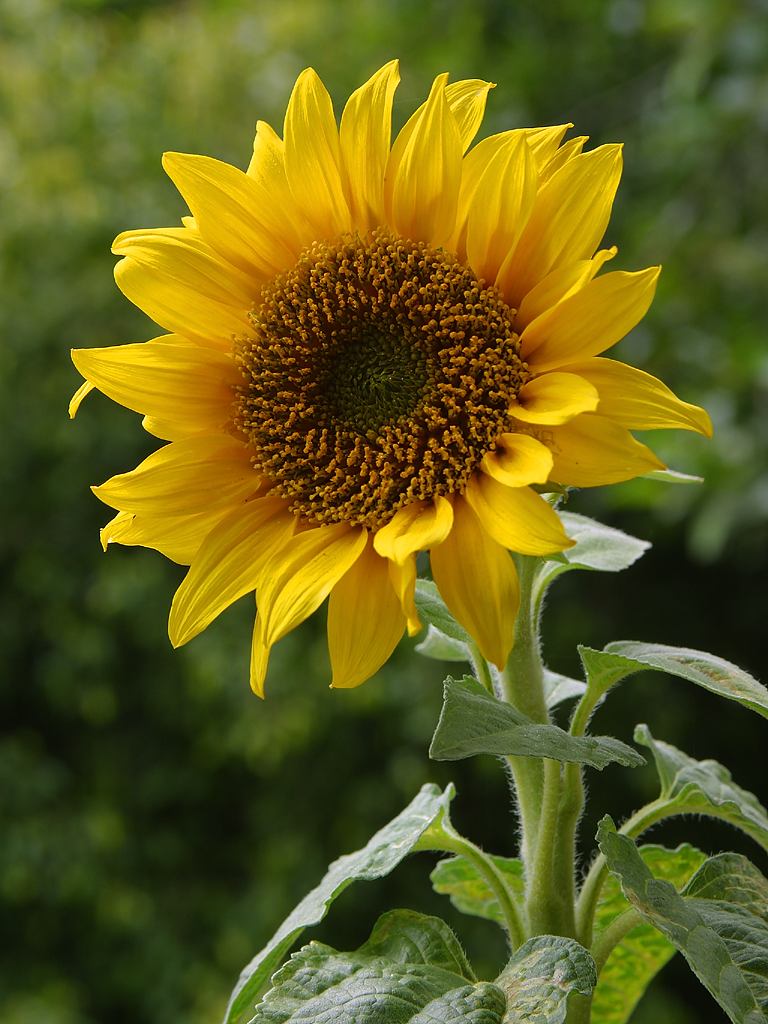
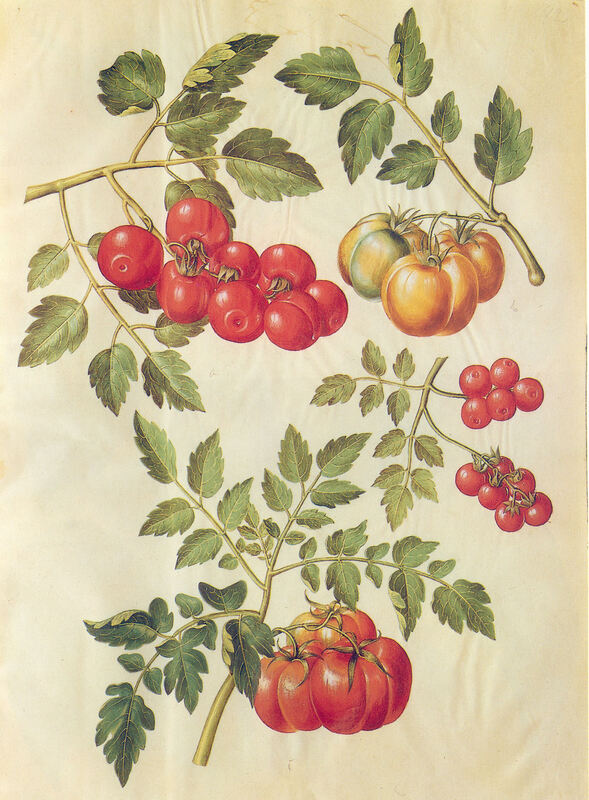
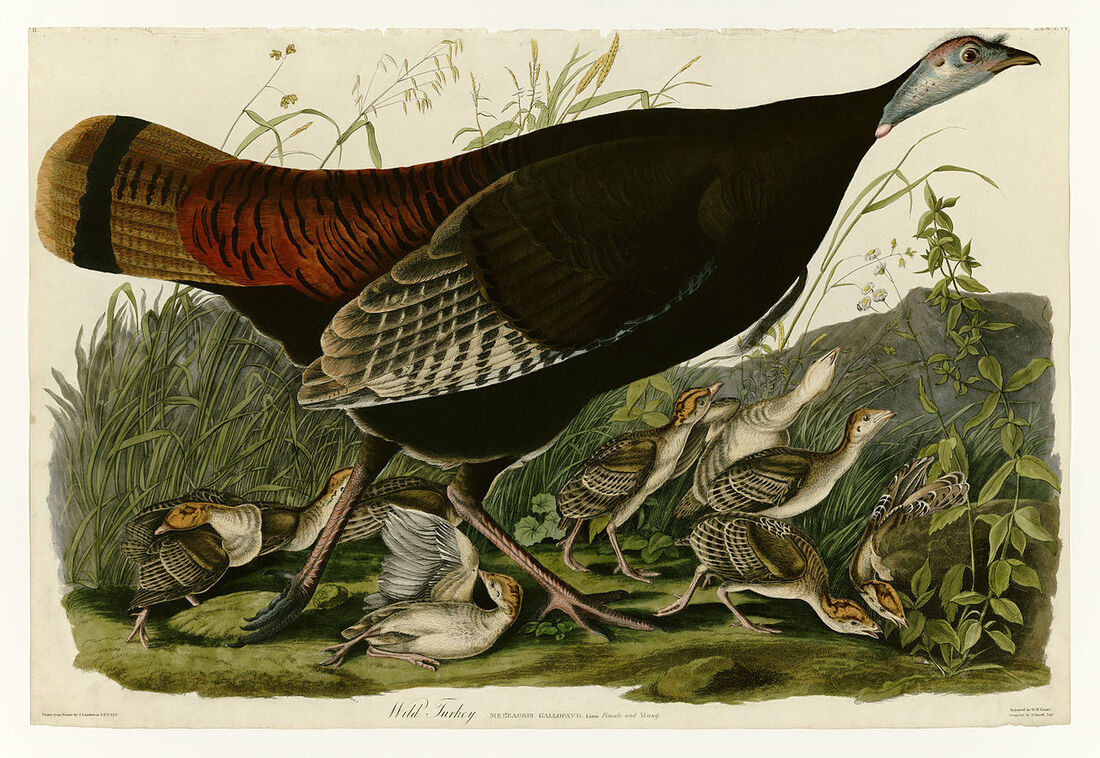
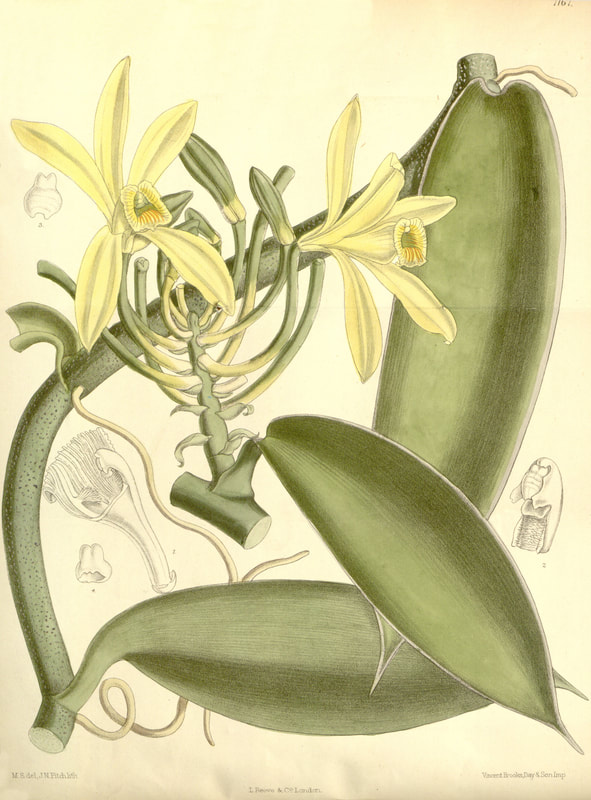
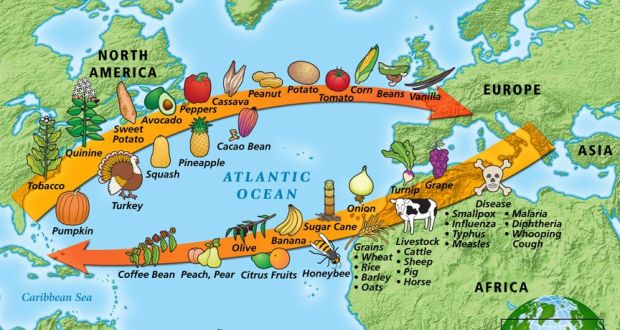
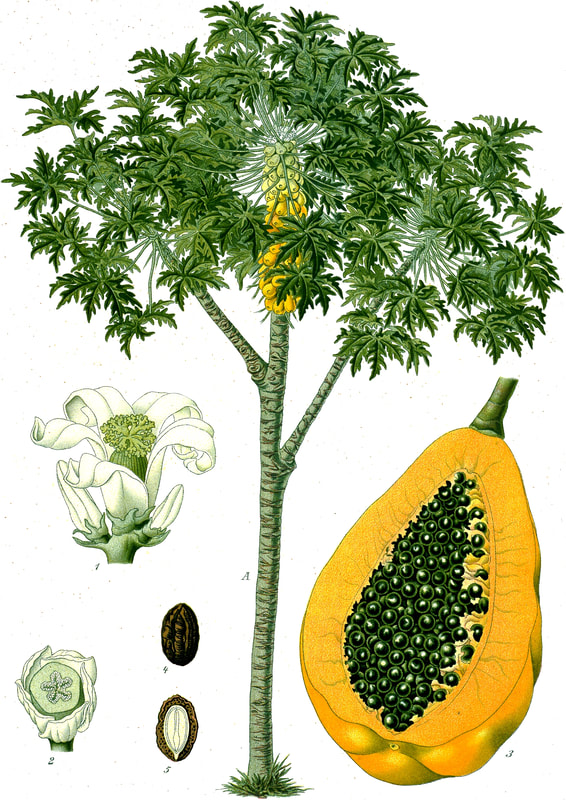
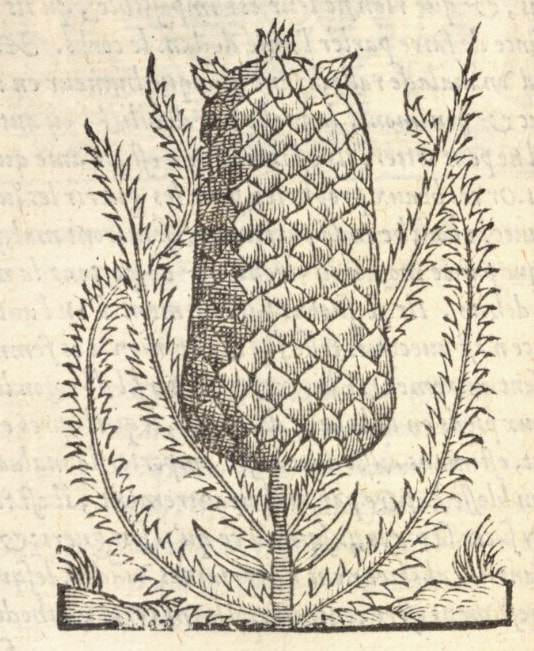
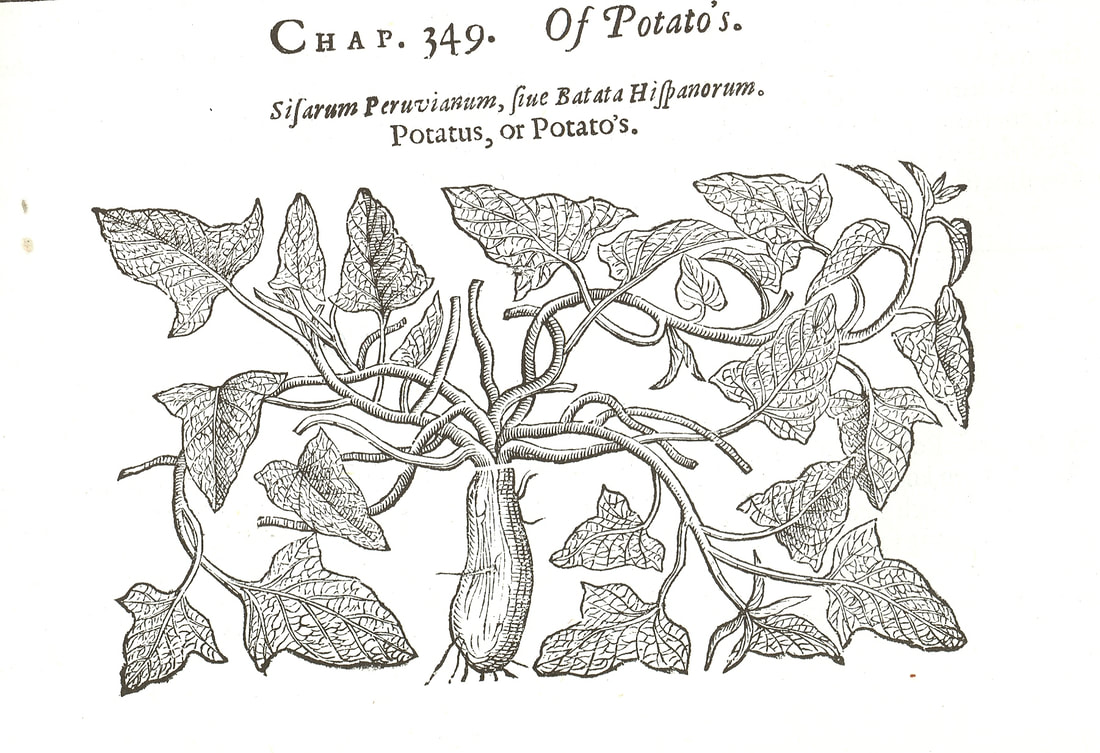
Today is Indigenous Peoples' Day. What, you thought it was Columbus Day? Well, for some people who don't know any better it still is, but Columbus was a pretty terrible person, driven by greed, and he didn't "discover" anything. Instead, he did things like sell 9 year old Taino girls into sex slavery, cut off children's hands if they didn't meet gold quotas, and generally committed genocide and slavery against every non-white person he met. He almost completely wiped out the Arawak-speaking peoples of the Caribbean, including the Lucayan people of the Bahamas and especially the Taino people of Hispaniola (present day Haiti and Dominican Republic). But as with most genocides, they're never 100% successful, and people throughout the Caribbean are descended from Taino people. One thing Columbus did lend his name to is a term called "The Columbian Exchange." The term was coined in the 1970s by historian Alfred W. Crosby, who studied the impacts of geography and biology on history, specifically the relationship between Europe and the rest of the world. Because Columbus was the first European to bring back many of the plants now used across the world, the exchange is named after him. Essentially, Irish potatoes, Italian tomato sauce, Swiss chocolate, Thai chilis, and a whole host of other important international foods are not actually from any of those places. They are ALL indigenous to North and South America and did not exist outside those continents prior to 1492. I'm going to catalog Indigenous American foodways in a minute, but first I want to emphasize how important it is to recognize that all of these foods are a result of Indigenous agricultural innovation. There is a tendency among many White folks to assume that these foods were just growing "wild" - and while that may be the case with some fruits, the vast majority were cultivated by Indigenous people, often in brilliant and surprising ways. And if you'd like to skip the list and go straight to figuring out where you can buy Indigenous foods and support Indigenous growers, harvesters, and producers, a good starting place is the list created by the Toasted Sister podcast. It's not comprehensive, but it's a great start. You can also check out this directory of certified American Indian Foods producers by the Intertribal Agricultural Council. You can even search by state! A small disclaimer - this is obviously not a complete list of Indigenous foods - I thought I would list the most influential foods globally and in the modern American diet. But I encourage you to use the magic of the internet to see what other foods you can find Indigenous to the area you live. And one final note - while it is important to preserve Indigenous foods and seeds, it's equally important to support the Indigenous people working to preserver them, like the Indigenous Seed Keepers Network. So while groups like Seed Savers Exchange are great, I encourage everyone to seek out Indigenous-owned and Indigenous-led companies and groups when choosing who to support. AmaranthWhere I grew up on the Northern Plains, in Lakota territory, one species amaranth is often known as "pigweed," and is considered a noxious weed by farmers. But Indigenous people know it as an important grain crop. Developed by the Aztec, amaranth was banned by the Spanish. The leaves of amaranth are also edible and some varieties are known as "callaloo," an important green vegetable for enslaved African peoples throughout the Caribbean and southern United States. If you're a gardener, "love-lies-bleeding" is a decorative variety of amaranth. There are dozens of varieties, but amaranth grains are often available for purchase from specialty stores and online. AvocadoAvocadoes, modern purview of hipsters, are actually an ancient fruit developed near Puebla, Mexico nearly 10,000 years ago (seriously, the world owes so much to Mexico in terms of agricultural innovation). The Indigenous residents of Puebla began cultivating the tree as much as 5,000 years ago. Modern-day avocadoes come in a whole host of varieties, but residents of the U.S. are most familiar with the Hass variety. Introduced to the American Southwest in the 1830s, avocado consumption in the United States didn't really take off nationally until the 1930s, influenced by California cuisine and used primarily in salads. Look in old cookbooks for references to "alligator pears," so named because of their bumpy green skin and pear shape. BeansBeans, especially climbing pole beans like the scarlet runner bean, are an important component of the Three Sisters style of agriculture, in which pumpkins or squash, corn, and beans are grown in concert with each other. The corn provides the stalk for beans to climb, the beans fix nitrogen in the soil for the corn and squash, and the broad leaves of the squash shade the ground, helping to prevent competing plants from growing and keeping the soil moist. Although some varieties of legumes did exist in Europe prior to the Columbian Exchange, notably chickpeas, peas, lentils, and broad beans, the introduction of the wide variety of cultivated Indigenous beans to Europe, especially kidney beans, including what would become the famous Italian cannelini. Black beans, pinto beans, and pink beans are other Indigenous varieties. Blueberries Image of the Weymouth variety of blueberries (scientific name: Vaccinium corymbosum), with this specimen originating in New Jersey, United States. Source: U.S. Department of Agriculture Pomological Watercolor Collection. Rare and Special Collections, National Agricultural Library, Beltsville, MD 20705, 1940. Lowbush blueberries (often marketed in grocery stores as "wild" blueberries) are native to North America, as other other blueberry-like fruits including huckleberries and juneberries (also known as serviceberries). Although these plants grew wild, blueberry barrens and other stands were often maintained by Indigenous peoples. Dried blueberry and cracked corn mush may have been served at the First Thanksgiving. Early European observers misnamed them "bilberries," after a relative native to Britain. In the early 20th century, highbush blueberries were cultivated from Indigenous blueberries in New Jersey. Highbush blueberries are bigger and therefore easier to harvest and ship than lowbush blueberries and are most often what you'll find in grocery stores today. CashewMost people probably associate cashews with Southeast Asia and Indian cuisines. But cashews are actually native to Brazil. The word "cashew" is a corruption of the word "acaju," which is Tupi for "nut." The Tupi people (of which there are dozens of sub-tribes) were who the Portuguese encountered when they first arrived there in the early 1500s. It was the Portuguese who brought the cashew to Goa, India in the late 1500s, where it thrived. Today, most commercially produced cashews are grown in India. ChiaMaybe you've noticed the trend for chia puddings these days. Or perhaps you're old enough to remember the Chia Pet craze of the 1980s. But the origins of chia are much older than you might suppose. Native to Central America, chia is thought to have been cultivated by the Aztecs as much as 3,500 years ago. An important staple crop throughout Mesoamerica, it was likely also used for religious purposes and may have been banned by Spanish colonizers for that reason. Thankfully, it survived. Chilis & PeppersChili peppers - from which all modern capsicums are derived, including bell peppers - were cultivated in Mexico as early as 6,000 years ago. Self-pollinating, chilis quickly spread throughout Mexico and Central and South America. Known in many countries by their cultivar name - capsicum - in the United States we call them "peppers" because Columbus and other Europeans associated them with the heat they had previously only known from black pepper. Like cashews, chili peppers were brought to Southeast Asia by Portuguese traders, where they quickly took hold as an essential part of many Asian cuisines. In the United States, New Mexico is best known for its production of chili peppers and its chili-eating heritage. Chilis are an essential ingredient in salsa, and Indigenous Mexican peoples use all different varieties (not just jalapenos and habaneros) for different levels of heat and flavor. ChocolateToday, chocolate is most often associated with Switzerland, Germany, and France. But its origins are ancient and date to Mesoamerica. The oldest references are for the Olmec peoples of central Mexico, who used it in religious ceremonies. But it was also used by the Maya and Aztec peoples, who both used cocoa beans as currency and used chocolate beverages in daily life and religious ceremonies. Although the origin of cacao plants is contested, they appear to have been common in Central America and actively cultivated as early as 5,300 years ago. Chocolate's chemical signature is often tracked as part of archaeological digs, and recent finds have suggested that its use and cultivation are earlier and more widespread than previously known. When it was introduced to Europe, Europeans treated it much like they did another dark, bitter beverage - coffee - by adding cream and sugar to it and drinking it for breakfast. By the 18th century, mechanization and slavery had made chocolate affordable to the middle classes. But it wasn't until the 19th century that chocolate bars, mixed with vanilla, sugar, dairy solids, and cocoa butter, came into widespread use. Corn (Maize)For most Americans, corn is hybridized sweet corn, popcorn, and maybe yellow or white cornmeal (or grits). But corn comes in thousands of different varieties and can be processed in hundreds of different ways. Did you know, for instance, that different varieties of corn - popcorn, dent, flint, flour, etc. - were cultivated for different uses? And that most corn can be eaten at all stages of development? And that "sweet" corn was originally just eating immature "green" corn before the sugars had turned to starch? Indigenous cooks also developed nixtamalization - a process whereby corn is soaked in wood ashes and water (i.e. lye) to de-hull and soften the corn. Nixtamalization also has the important additional benefit of releasing the niacin (Vitamin B3) from the corn so that it can be processed by the body. Niacin deficiency, also known as pellagra, plagued 19th and early 20th century White Americans, who did not know how to process the corn properly. Corn was developed from a grass native to south central Mexico called teosinte - which is still used today in Mexico as a fodder for livestock. As cultivated varieties spread throughout North America, they took on different characteristics as they cross-pollinated with other varieties and native species of teosinte. Corn is wind pollinated, meaning that it cross-breeds easily. Today, corn's global dominance is almost entirely related to its role as livestock feed, especially with beef. Sadly, beef cattle are not well suited to being raised on corn, and "corn fed beef," which is designed to put on a lot of fat for your "well-marbled" steak, is actually extremely destructive to bovine digestive systems. Not to mention unhealthy for humans, too. American agricultural subsidies for corn, which allow food processors to purchase it for less than it costs farmers to produce, have also allowed the proliferation of its use as an industrial food, notably corn syrup, but corn is now in almost everything we eat. And not in a good way. If you want to help Indigenous producers, buy Indigenous-grown Indigenous corn products. Here in New York, you can buy Iroquois White Corn. Don't feel like eating corn but want to help? Support Indigenous seedkeeper groups. Can't find one in your area? Donate to the Indigenous Seedkeeper's Network. CranberriesToday, cranberries are most often associated with Thanksgiving and New England, but cranberries are native to the northeast of North America and were used often by Indigenous peoples in those areas. Although a variety of cranberry is native to the bogs of Britain, and the Scandinavian lingonberries are a relative, the vast majority of modern cranberry consumption is based on species native to the U.S. and Canada. Maple Syrup & SugarMaple Syrup is one of the few sweeteners native to North America (honeybees, sugar cane, sorghum, and sugar beets are all imported). First used by Indigenous peoples in the Northeast, it is unclear which tribes first started use of maple sap as a sweetener. One Haudenosaunee/Iroquois legend indicates that the people first observed red squirrels cutting into the bark of maple trees and returning to drink the sap that flowed out. This has since been confirmed by scientific observation of squirrel behavior. Maple syrup and sugar was made either by freezing the water out of the sap, or by boiling with heated rocks. European colonists were quick to adopt maple sugaring as an important source of late winter calories and shelf-stable year-round sweetener. Although for some reason in the United States maple products are associated with fall, maple sugaring time is usually in March, when daytime temperatures rise above freezing, and fall below freezing at night - perfect conditions for optimum sap production. PapayaThe native range of the papaya is from southern Mexico to northern South America, although it has been naturalized throughout the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico. With a quick maturity - some papaya can produce fruit after just one year - Europeans spread the plant to other tropical regions around the world where it is widely used in many different stages of ripeness, both cooked and raw. PeanutsThe archaeological record of peanut cultivation is not clear, but it is clear that it was present in Brazil and Central America in the 16th century when European explorers arrived in South America. The peanut is not actually a nut - it is a legume and more closely related to beans than, say, pecans. But its culinary importance grew once it was imported by Europeans to Africa and Asia. The peanut actually came to North America by way of enslaved Africans, who carried it with them as they were stolen from their homelands. The peanut was largely regarded as animal fodder by Europeans, and used in subsistence farming by enslaved Africans and African-Americans in the U.S. In the late 19th century, a number of people, including John Harvey Kellogg and Heinz, were filing patents for peanut-butter-like substances. Ironically, George Washington Carver, African-American plant scientist and the man most associated with peanut butter, didn't actually invent it. Today, about the only people who don't enjoy peanuts much are Europeans, which is ironic given their role in spreading them globally. PecanNative to North America, the pecan is one of my favorite nuts. Its native range ran from New England to Mexico and was widely used by Indigenous peoples. The word "pecan" likely comes from a 16th century European corruption of the Algonquian word "pacane," describing nuts that required stones to crack. Hickory nuts (also known as butternuts) and black walnuts are in the same family as pecans. PineappleAlthough most Americans associate pineapples with Hawaii, they are actually native to the Paraguay River basin, which stretches between modern-day Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay, and Argentina. Pineapples were cultivated by the Maya and Aztecs and Europeans first encountered them in the 15th century. Named the "pine apple" because of its resemblance to a pine cone and its status as a fruit, Europeans were able to grow some pineapples in greenhouses. In the 18th century, the pineapple was a symbol of hospitality and wealth and were much smaller than modern-day cultivars. Pineapple plantations were first installed by White Americans in Hawaii in the 1880s. James Dole made his fortune with pineapple plantations, processing, and canning innovations, which introduced the pineapple to ordinary Americans across the country. PotatoesWhat would Europe be without the potato? And yet, this starchy tuber, which spread throughout the Andes mountains prior to European contact, is originally from the border of modern-day Peru and Bolivia and dates back as far as 8,000 years ago. Cultivated from the wild tuber by Indigenous agriculturalists, over 5,000 varieties now exist. Potatoes were the staple crop of the Inca, who built their empire on it. Andean Indigenous peoples used it in all the usual ways, but also pioneered a special preservation technique called chuño, whereby the potatoes were frozen and dried in a way that made them very light and allowed them to keep for years. Chuño was usually prepared as part of a stew and was an important cash crop for Indigenous farmers. Prior to its introduction to Europe, most of the poorer classes relied on turnips and rutabaga for starchy bulk calories. But the potato was not only more palatable, it was more prolific, easier to grow, and it kept longer in storage. The shift to potatoes throughout Northern Europe in particular meant that the advent of potato blight in the mid-19th century, particularly in subjugated Ireland, started a mass migration of Europe's poor to the nations which had fed them so well for so long. QuinoaAlso native to the Andes and Peru, quinoa (pronounced "keen-wah"), is a member of the amaranth family. Used as a cereal crop by the Inca and other Indigenous peoples in the Andes mountains, quinoa has been in cultivation for as many as 5,000 years. When the Spanish arrived, determined to stamp out Incan culture, quinoa almost disappeared, but it persisted. Its "discovery" by White Americans interested in "superfoods," the price of this essential Indigenous grain actually skyrocketed. Whether or not this is good for Indigenous farmers is a matter of some debate, but when in doubt, be sure to buy from Indigenous producers. Squash & PumpkinAlong with corn and beans, squash make up the famous "Three Sisters" of Indigenous foodways. One of the oldest cultivated crops of the Americas, dating back as many as 10,000 years ago (before maize and beans), squashes are native to the Andes and Mesoamerica and wild varieties actually predate human inhabitation on the continents. Their cultivation was widespread throughout North and South America prior to European contact. All global varieties of squash, including pumpkins, zucchini, and decorative gourds, originated in the Americas. The word "squash" is an English corruption of the Narragansett word "askutasquash" meaning "a green thing eaten raw." Today, pumpkins (a word for a particular kind of large, round, orange squash that doesn't actually have an official classification) are mostly associated with Thanksgiving and New England foodways, although in the 19th century they were also stereotypically associated with slavery. They were one of the Indigenous foods featured in the first "American" cookbook, published by Amelia Simmons in 1796. SunflowerSunflowers are also native to North America, thought to have been cultivated near present-day Arizona and New Mexico around 3000 BC. Cultivated for their oily seeds and tuberous roots (also known as sunchokes or "Jerusalem artichokes"), sunflowers were also sometimes used as dyes. Although they were an important crop for Indigenous peoples, they were not in widespread use by European-Americans until their popularization in 19th century Russia, where they had been imported. Today, North and South Dakota are the biggest producers of sunflowers in the US and sunflower seeds, "sunbutter" and sunflower oil are popular modern uses. Not so much with the "sunchoke," although the tubers are regaining some popularity. Sweet PotatoSweet potatoes are native to Central America. Although called "potatoes" and sometimes "yams," they are not related to either plant. Sweet potatoes are more closely related to morning glory and bindweed. Sweet potatoes were spread across the Pacific nearly 400 years before Columbus by Polynesians, who brought the vine back with them. It was the Spanish and the Portuguese, however, who spread the sweet potato to the Philippines and Japan, respectively. The Spanish also brought the sweet potato to West Africa, where it was adopted, but not without some derision as its taste. The yam is native to Africa, which is likely why so many Americans, especially African-Americans, call sweet potatoes "yams." TomatoWhich is more authentic? Italian tomato sauce, or Mexican salsa? Hate to break it to you, but the Mexicans have the ayes on this one. Wild tomatoes are native to Western Mexico and were originally tiny, sour, and hard. Careful cultivation by Indigenous people led to thousands of more edible varieties, including husk tomatoes ranging from tomatillos to ground cherries. In Nahuatl (the Aztec language), "tomatl" was used to reference green tomatoes like tomatillos, and "xitomatl" was used for red varieties. The Spanish translated it as "tomate" and hence the term "tomato." When brought back to Europe, the bright red fruits were originally identified as a type of eggplant (both are members of the nightshade family), it garnered the nickname "love apple," and was originally considered poisonous. Although it was cultivated as a decorative plant, it was not in widespread use in Europe until the mid-18th century. It's widespread adoption in Italy was likely connected to nationalist sentiments in the 19th century and its association with the color red in the flag of Italian unification. In the United States, Thomas Jefferson may have helped popularize the tomato outside of the American southwest. And his relative by marriage, Mary Randolph, featured tomatoes in her Virginia Housewife cookbook, published in 1824. By the end of the 19th century, tomatoes became a popular American preserve, providing color, acidity, and sweetness to the typical American table. TurkeyIndigenous to North America, turkeys have been consumed by Indigenous peoples for centuries. Turkeys were domesticated in Mesoamerica as early as 800 BC. The Spanish brought back domesticated Aztec turkeys to Europe, where they quickly joined the European game bird lexicon. Associated with Christmas in Britain as early as the 17th century, the British Christmas goose persisted until the 20th century. In the United States, turkey is most commonly associated with Thanksgiving, although it is also often consumed at Christmas. Turkeys are one of the only indigenous American meat animals widely adopted in Europe and elsewhere. The name "Turkey" is likely associated with how Europeans were first introduced to turkeys - either through trade with the Middle East, or in association with guinea fowl as a game bird, introduced via Turkey. Domesticated turkeys are thought to have been descendants of Aztec domesticated birds reintroduced to North America via Europe. The turkeys purportedly eaten at the First Thanksgiving would have almost certainly been wild varieties, however. A shift to large scale commercial poultry production in the early 20th century has helped introduce turkey into the American diet through things like sliced deli turkey. The virtual disappearance of wild turkeys from New England due to deforestation meant that they had to be reintroduced to New England, an effort that began in the 1960s. VanillaVanilla is an orchid native to the Caribbean and south Central America. Cultivated by pre-Columbian Maya people, it was widely adopted by subsequent Indigenous peoples, including the Aztecs, who added it as a flavoring agent to their chocolate beverages. Attempts to cultivate vanilla in Europe were unsuccessful, largely because vanilla is naturally pollinated only by a native species of bee. An boy named Edmond Albius, enslaved on the Island of Reunion, pioneered a hand pollination technique that allowed vanilla to spread across the globe, including to the islands of Tahiti and Madagascar. Wild RiceWild rice, known in Anishinaabe/Ojibwe as "manoomin," is, indeed, a wild rice. Growing in marshy lakes, truely wild rice is harvested by hand from the wild. Wild rice is central to Anishinaabe culture, and one legend indicates that Ojibwe people emigrated from the Atlantic coast to the "place where food grows on the water." Although Northern wild rice is the most common, other two other varieties are native to North America - one in Florida and one in Texas. Suggestions to grow wild rice commercially were suggested as early as the mid-19th century, but it was not attempted on any scale until the 1950s. Commercially cultivated "wild" rice is now a great source of controversy, as is the genetic modification of wild rice. Opponents argue that commercial wild rice conflicts with Indigenous food sovereignty and treaty rights. True wild rice can also be endangered by relaxed water pollution standards, oil pipelines, and more. Indigenous people were rarely if ever involved in the research and are not beneficiaries of commercial varieties. For reasons of taste and to support Indigenous tribes and businesses, I strongly recommend that you source your wild rice from Indigenous producers. ConclusionPhew! That is a LOT of influential foods developed by Indigenous Americans. I hope you learned something with this catalog - I know I did. And I hope you'll support Indigenous food producers by purchasing direct whenever you can. Thanks to the magic of the internet, that's now possible more than ever. And for those of you interested, I'm planning a couple more posts (and a few talks) about the influence of pumpkins, corn, wild rice, and more. So stay tuned! What's your favorite Indigenous American food? The Food Historian blog is supported by patrons on Patreon! If you found this article interesting, useful, and/or thought-provoking, join us for awesome members-only content like free digitized cookbooks from my personal collection, e-newsletter, and even snail mail from time to time!
1 Comment
Thanks to everyone who joined me last night for Food History Happy Hour live on Facebook. This week, inspired by the cold, rainy weather we've been having lately, we "visited" the American Southwest with help from the Desert Healer cocktail from the 1946 Roving Bartender. We discussed Mexican food in America, including the cookbook California Mexican-Spanish Cook Book, published in 1914 by home economist Bertha Haffner-Ginger. We also talked about burritos, corn and nixtamalization (including hominy and tortillas), savory fruit salads, sauces, including celery sauce, macaroni and cheese, 19th century pickles, jicama, pickled herring, lutefisk and cod (small correction, mahi-mahi is dolphinfish, not tilapia), and we decided that next week's topics will be 19th century sauces and pickles!
Although cocktails called "Desert Healer" are all over the internet, I couldn't find any history behind either the name or the cocktail. I'm guessing it's just one of those cocktails that someone made up and it took off. If you like your cocktails on the sweeter side, but still with some complexity of flavor, you will probably love this one.
I found this recipe in the Roving Bartender (1946). I did get the recipe slightly wrong and only did a third of an ounce of cherry brandy, but more cherry brandy would have been even better! Desert Healer Cocktail (1946)
2 cubes ice
3 oz. orange juice 1/2 oz. cherry brandy 1 oz. gin (I used American gin, but any is fine) Place ingredients in a 10 oz. glass in order, then fill with ginger ale. Drink with a straw. I found this to be quite delightful and would definitely make it again, especially since it's such a nice way to use up the cherry bounce I made.
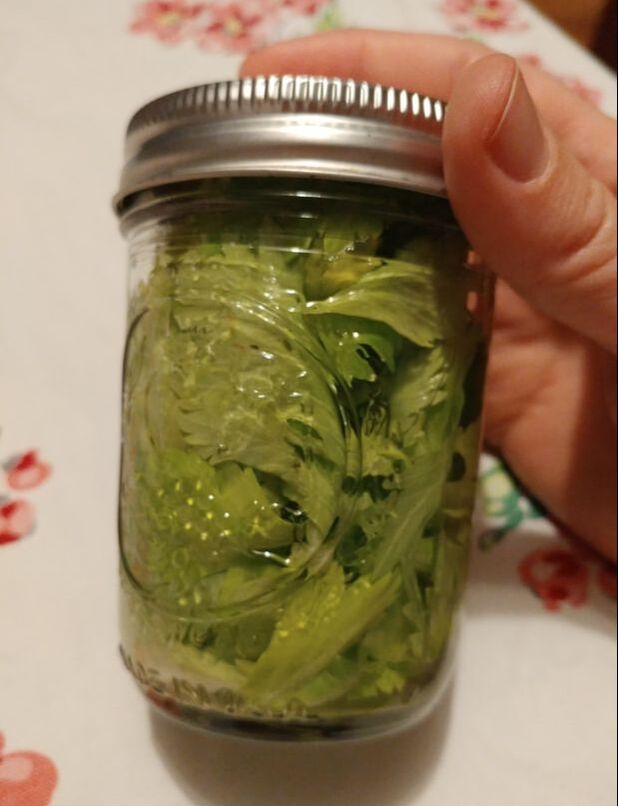
And, of course, given all of our discussion of celery and someone's idea that I make a cocktail with celery sauce (yuck), I thought that infusing gin with celery was a delightful idea, and it just so happened that I had cut up the remains of a head of celery for crudite to go with supper. So I had lots of delightfully fresh leaves and a few stalks leftover. Into a half pint jar they went with some gin poured over top and we'll let it steep until next week, when I'll have to decide what kind of gin cocktail I want to make with it.
As mentioned last week, the bar cabinet tour is still on the list, but I might do a recorded tour instead of a live one as I think it will be easier to manage. So stay tuned, and hope to see you all next week!
If you liked this post and would like to support more Food History Happy Hour livestreams, please consider becoming a member or joining us on Patreon. Members and patrons get special perks like access to members-only content.
|
AuthorSarah Wassberg Johnson has an MA in Public History from the University at Albany and studies early 20th century food history. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|









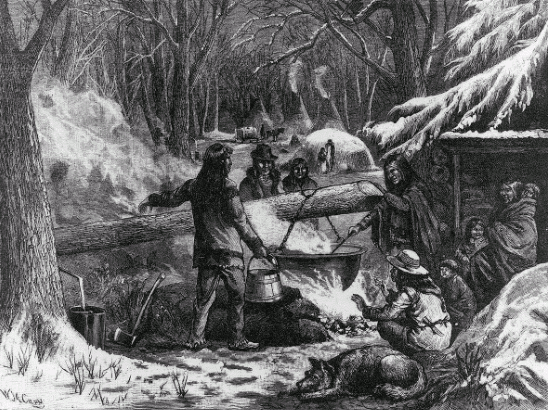













 RSS Feed
RSS Feed