|
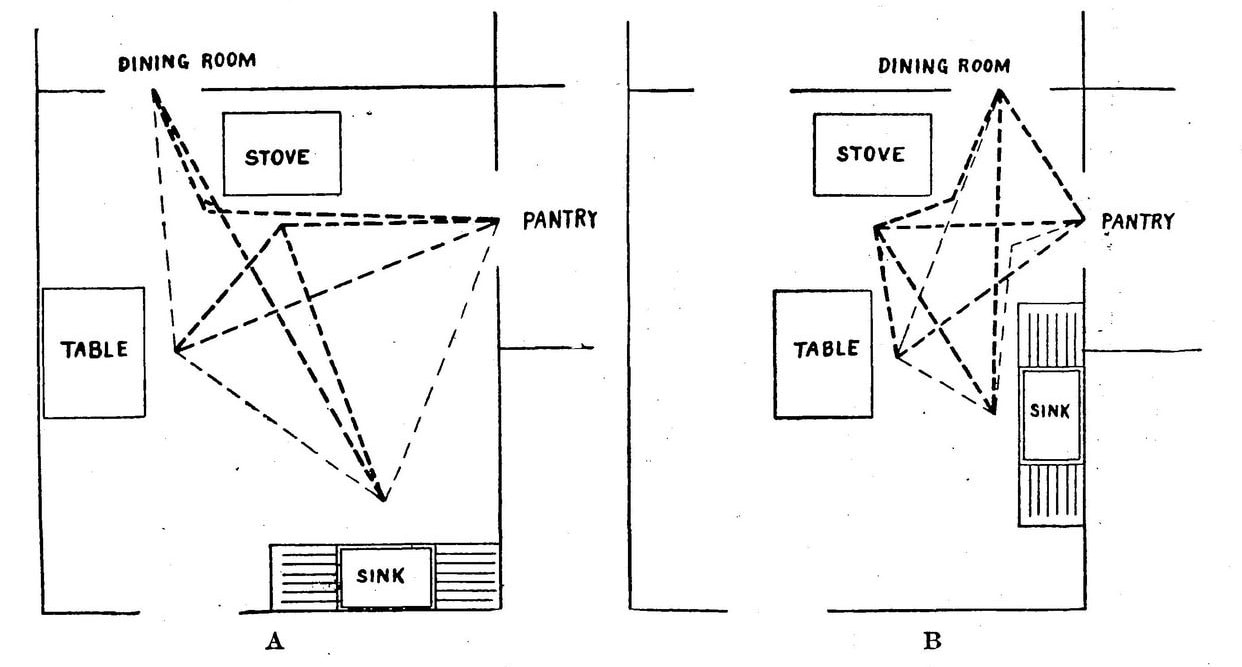
The other night I introduced a friend to one of my favorite YouTube videos ever. It’s a 1949 film put out by the United States Department of Agriculture’s Home Economics. You can watch the whole thing below: I love this film for a variety of reasons, but the primary one is how incredibly FUNCTIONAL this kitchen is. Not everything is perfect. The “messaging center” is too close to the stove for me – too able to collect splatters and grease from cooking. And the table, while nice, I think would have been better served by a more efficient built-in breakfast nook. But everything else? I LOVE IT. The storage is incredible. Everything is built with thought to use and efficiency. From the cooking and cleaning activities to the storage. And while the cabinets aren’t the prettiest, keep in mind that the design is meant to be built by farmers and handy homeowners – not professional contractors. Learn more about the film and the pamphlet for the Step-Saving Kitchen. This kitchen design is the culmination of several decades of work studies. During the Progressive Era, American interest in science began to increase, and scientific theories were applied to everything from factories to households. The Efficiency Movement was part of this application of scientific principles to everyday life. Led by mechanical engineer Frederick Winslow Taylor, the movement posited that everyday life, from industry to government to households, were plagued by inefficiencies, which wasted time, energy, and money. It also influenced the ecological conservation movement, a reaction to overuse of natural resources, and President Teddy Roosevelt was a known proponent. The movement, which became known as “Taylorism,” was hugely influential and spurred Progressive Era trust in experts and authorities that continued until the 1960s. Nowhere was Taylorism probably more influential than in the home economics movement, which advocated for efficiency in everything from nutrition to childrearing to household design. And that was thanks in part to the work of Christine Frederick, who in 1912 took Taylor’s principles and applied them to the household with a series of articles on “New Housekeeping” she wrote for the Ladies’ Home Journal. She started a Taylor-style efficiency laboratory in her own home kitchen and went on to publish several more books on the subject, including the 1919 Household Engineering: Scientific Management in the Home. Another influential advocate of household efficiency was psychologist Lillian Gilbreth. With her husband Frank Gilbreth, the two created a partnership to take Taylor’s ideas and apply them to industrial spaces, developing time-and-motion studies. Today, you might know them best as the parents who starred in the book (and subsequent films) Cheaper by the Dozen. After Frank’s untimely death in 1924, Lillian encountered discrimination in the engineering field, and began to turn her talents toward the domestic sphere. Partnering with Mary E. Dillon, president of the Brooklyn Borough Gas Company (and the first female utility president in America), Gilbreth and Dillon developed the kitchen work triangle, which advocated for a step-saving triangle between sink, stove, and refrigerator. Part of Gilbreth’s Practical Kitchen, the new design was revealed at the Eighth Annual Exposition of Women’s Arts and Industries on October 1, 1929. Eleanor Roosevelt was one of the speakers. Many of these principles were adopted by government organizations like the USDA. As early as the 1909, with the federal government’s Country Life studies, the plight of farm women and their poorly designed, technology-lacking kitchens came to light. The USDA’s Farmer’s Bulletin No. 607, “The Farm Kitchen as Workshop,” published in 1921 by Anna Barrows, outlined some of the concerns about kitchen efficiency and how to correct them. Page 10 of the bulletin illustrated the difference in closing the distances between workspaces – a star shape similar to the kitchen work triangle resulted. Several Congressional Acts brought federal funding to these studies. The Smith-Lever Act of 1914 mandated home economics instruction at land grant colleges. The Purnell Act of 1925 allocated federal funding into vitamin research and research of rural home management. These types of studies flourished under the federal funding and in my opinion placed overdue emphasis on the safety, sanitation, comfort, and efficiency of the home. All of these efficiency studies contributed to the result of the 1949 kitchen I love so much. But what happened? Why do modern kitchens seem to ignore the best research of the past? Today, there is far less government investment in domestic study – either from the USDA or public universities. The USDA’s Bureau of Home Economics was shuttered in 1962. Some of its personnel were shifted to the Nutrition and Consumer-Use Research department under the auspices of the USDA’s Agricultural Research Service. Some consumer-based research regarding food was absorbed by the FDA. But the kitchen research seems to have largely been abandoned. Some universities, like at Cornell, have continued to offer household design programs as subsets of architectural programs. But the federal funding is gone. Which is a shame, because our household lives seem to have suffered for it. One rule that has been adopted most widely is the kitchen work triangle. But not always. For instance, my kitchen doesn’t have one – the refrigerator, stove, and sink are all in a line. The only triangle is that my primary work surface is on the other side of my galley kitchen. And don’t even get me started on the ergonomics of storage. Those seem to have been discarded wholesale. One ray of light has been the resurgence of roll-out shelves. But even these are few and far between, likely because they are more expensive than traditional fixed shelving. And yes, dear reader, here, I think, is the rub – efficient kitchens must be custom designed. And in our cookie-cutter, prefab world, both design and customization are expensive. In addition, many of today’s kitchens are designed more for show, or occasional entertaining, rather than daily life. Which is an unfortunate reflection of how many Americans cook (or don’t). Case in point: the disappearance of the pantry – the one final thing that 1949 kitchen doesn’t have (it’s presumably in the cellar in the film) that I’d want. At any rate, if I ever win the lottery, you know what kind of kitchen I’ll be building. What aspects of the 1949 Step-Saving Kitchen did you like best? What would your dream kitchen look like? Sources & Further Reading
The Food Historian blog is supported by patrons on Patreon! Join us for awesome members-only content like free digitized cookbooks from my personal collection, e-newsletter, and even snail mail from time to time!
1 Comment
Sarah
12/15/2023 06:57:54 pm
It seems to me in the film that plans for this kitchen could be had by the general public. I don’t suppose you know where they could be acquired now?
Reply
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorSarah Wassberg Johnson has an MA in Public History from the University at Albany and studies early 20th century food history. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed